
Extreme Networks ExtremeSwitching X480 48-port Switch
Scalable and Versatile Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet Switch

48 10/100/1000BASE-T, 4 100/1000BASE-X unpopulated SFP (shared), No PSU with two unpopulated PSU slots, one VIM2 slot, ExtremeXOS Advanced Edge license
Our Price: Request a Quote
48 100/1000BASE-X unpopulated SFP, No PSU with two unpopulated PSU slots, one VIM2 slot, ExtremeXOS Advanced Edge license
Our Price: Request a Quote
Click here to jump to more pricing!
Please Note: All Prices are Inclusive of GST
Overview:
The Summit X480 series switch is a versatile, high-end Ethernet switch for data center, enterprise aggregation, and Carrier Ethernet deployments. Summit X480 helps optimize application performance for a variety of network deployments with its rich features and high scalability.
Summit X480 provides high density for Gigabit Ethernet in a small 1RU form factor for up to 48 ports in one system and 384 ports in a stacked system using backward compatible SummitStack™, high-speed SummitStack128 running at 128 gigabits per second, or SummitStack-V, which utilizes 10 GbE ports as stacking ports, enabling the use of standard cabling and optics technologies used for 10 GbE. Summit X480 also offers 10 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity for up to six ports in one system and 16 ports in a stacked system with the industry-standard XFP interface.
For emerging demands from voice/data convergence and storage, Summit X480 provides highly scalable Layer 2/3 switching and MPLS/H-VPLS by supporting up to 512K Layer 2 MAC addresses or 512K IPv4 Longest Prefix Match routing tables. Summit X480 enables data center, enterprise and Carrier Ethernet aggregation and core backbone deployment in AC-powered and DC-powered environments.
Summit X480 simplifies network operation with the ExtremeXOS modular OS, available across a wide range of Extreme Networks Ethernet switches. The ExtremeXOS operating system provides high availability and simplicity with one OS everywhere in the network.
Target Applications
- Top-of-rack switch for servers in enterprise data centers
- High-performance core switch for a small network
- High-performance gigabit aggregation switch in a traditional three-tiered network
- Carrier Ethernet network switch that can aggregate connectivity for first mile access concentrators such as DSLAM and CMTS
Features:
High Performance Switching and Routing
- 48-port Gigabit Ethernet or 24-port gigabit and 2-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet connectivity in a 1RU form factor
- Optional 4-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) to provide 40 Gbps uplinks
- Optional 40 Gbps stacking for up to eight switches in a stack to provide up to 384 Gigabit Ethernet connections in one logically integrated unit
- Optional 128 Gbps stacking for up to eight switches in a stack to provide high-speed stacking
- Optional stacking via 10 GbE ports (SummitStack-V), or optional SummitStack-V80 80 Gbps stacking
- Supports Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching, as well as MPLS/H-VPLS
High Scalability in a 1RU Compact Switch
- Up to 512K MAC address support for scalable Layer 2 networks
- Up to 512K IPv4 routes for scalable Layer 3 networks
- Up to 60K Access Control Lists (ACLs) for secure networks
- ExtremeXOS® modular OS for highly available network operation
- Carrier-grade redundant networking protocol including Ethernet Automatic Protection Switching (EAPS)
- Internal redundant AC/DC power supply and field replaceable/hot swappable fan tray
Comprehensive Security Management

High-Performance and Highly Scalable Switching and Routing
Summit X480 offers core-class intelligent switching and routing with exceptional port density and high-performance stacking technology powered by the ExtremeXOS modular OS. With its high performance switching and routing, Summit X480 helps enhance the data center, Carrier Ethernet and enterprise aggregation network.
High-Performance Switching and Routing
Summit X480 is available in three different port configuration options: 24-port Gigabit Ethernet and 2-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet (Summit X480-24x), 48-port copper Gigabit Ethernet (Summit X480-48t), or 48-port fiber Gigabit Ethernet (Summit X480-48x). All front panel ports run at non-blocking, wire-speed performance and can carry wire-rate traffic towards the Versatile Interface Module-2 (VIM2) slot. Summit X480 offers flexible configuration by using optional VIM2 modules which are: 4-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet Module (VIM2-10G4X), 2-port SummitStack Module (VIM2-SummitStack), 2-port SummitStack128 Module (VIM2-SummitStack128) or 2-port SummitStack-V80 Module (VIM2-SummitStack-V80) (see Figure 1: Port configuration options for Summit X480 switches).
Flexible Port Configuration
Summit X480 offers flexible port configurations from standard configuration to optional VIM2 modules. For Summit X480-24x, half of the Gigabit Ethernet ports can handle dual personality- select from either 10/100/1000BASE-T copper Gigabit Ethernet or 100/1000BASE-X fiber Gigabit Ethernet connectivity. In the case of Summit X480-48t, the last four Gigabit Ethernet ports are configured as dual personality ports to provide flexibility between copper and fiber Gigabit Ethernet.
Through the VIM2 slot, Summit X480 can add an additional four 10 Gigabit Ethernet or SummitStack stacking ports. For stacking, depending upon the needs for bandwidth across the units in a stack, Summit X480 supports 40 Gbps SummitStack, 80 Gbps SummitStack-V80 or 128Gbps SummitStack128 through VIM2 option modules (See Figure 2: Summit X480-24x flexible port configuration). A third option, SummitStack-V, utilizes 10 GbE ports as stacking ports.
Summit X480 supports flexible 10 gigabit optical transceivers such as 10GBASE-SR, LR, ER and ZR as well as tunable DWDM. Tunable DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) support allows service providers and others to tune XFP 10 Gigabit Ethernet optics to a specific frequency, reducing the need for additional fiber runs and XFP sparing. Digital Diagnostics Monitoring Interface support allows service providers to monitor and diagnose pluggable optics in real-time.
SummitStack - High-Performance Stacking
Summit X480 supports SummitStack, which provides 40 Gbps (VIM2-SummitStack), 80 Gbps (VIM2-SummitStack-V80) or 128 Gbps (VIM2-SummitStack128) of stacking bandwidth. High-speed 128 Gbps stacking is ideal for demanding applications where a high volume of traffic traverses through the stacking links, yet bandwidth is not compromised through stacking. High-speed stacking is very useful in applications such as top of rack when stacked with Summit X480 and Summit X650 (requires optional conversion cable) and gigabit aggregation in large enterprise or data center networks. With the longer stacking cables such as 5-meters, stacking can be configured through different racks horizontally in a row (see Figure 3) as opposed to typical stacking system installed vertically in a rack.
SummitStack-V - Flexible Stacking Over 10 Gigabit Ethernet
SummitStack-V capability utilizes 10 GbE ports as stacking ports, enabling the use of standard cabling and optics technologies used for 10 GbE such as XFP, SFP+, 10GBASE-T and XENPAK. SummitStack-V provides long-distance stacking connectivity of up to 40 km while reducing the cable complexity of implementing a stacking solution. SummitStack-V enabled 10 GbE ports must be physically direct-connected. SummitStack-V is compatible with Summit X450e, X450a, X460, X480, X650, X670 and X670V switches running the same version of ExtremeXOS.
| VIM Options | None (default option) | VIM2-10G4X | VIM2-SummitStack | VIM2-SummitStack-V80 | VIM2-SummitStack128 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summit X480-24x | • 24 x 100/1000BASE-X (SFP) • 12 x 10/100/1000BASE-T (shared with the last 12 SFP ports) • 2 x 10GBASE-X (XFP) |
• 24 x 100/1000BASE-X (SFP) • 12 x 10/100/1000BASE-T (shared with the last 12 SFP ports) • 6 x 10GBASE-X (XFP) |
• 24 x 100/1000BASE-X (SFP) • 12 x 10/100/1000BASE-T (shared with the last 12 SFP ports) • 2 x 10GBASE-X (XFP) • 2 x SummitStack |
• 24 x 100/1000BASE-X (SFP) • 12 x 10/100/1000BASE-T (shared with the last 12 SFP ports) • 2 x 10GBASE-X (XFP) • 2 x SummitStack-V80 |
• 24 x 100/1000BASE-X (SFP) • 12 x 10/100/1000BASE-T (shared with the last 12 SFP ports) • 2 x 10GBASE-X (XFP) • 2 x SummitStack128 |
| Summit X480-48t | • 48 x 10/100/1000BASE-T • 4 x 100/1000BASE-X (shared with the last 4 10/100/1000BASE-T ports) |
• 48 x 10/100/1000BASE-T • 4 x 100/1000BASE-X (shared with the last 4 10/100/1000BASE-T ports) • 4 x 10GBASE-X (XFP) |
• 48 x 10/100/1000BASE-T • 4 x 100/1000BASE-X (shared with the last 4 10/100/1000BASE-T ports) • 2 x SummitStack |
• 48 x 10/100/1000BASE-T • 4 x 100/1000BASE-X (shared with the last 4 10/100/1000BASE-T ports) • 2 x SummitStack-V80 |
• 48 x 10/100/1000BASE-T (shared with the last 4 10/100/1000BASE-T ports) • 2 x SummitStack128 |
| Summit X480-48x | • 48 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP | • 48 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP • 4 x 10GBASE-X (XFP) |
• 48 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP • 2 x SummitStack |
• 48 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP • 2 x SummitStack-V80 |
• 48 x 100/1000BASE-X SFP • 2 x SummitStack128 |
Figure 1: Port Configuration Options for Summit X480 Switches
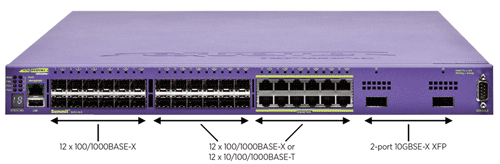
Figure 2: Summit X480-24x Flexible Port Configuration
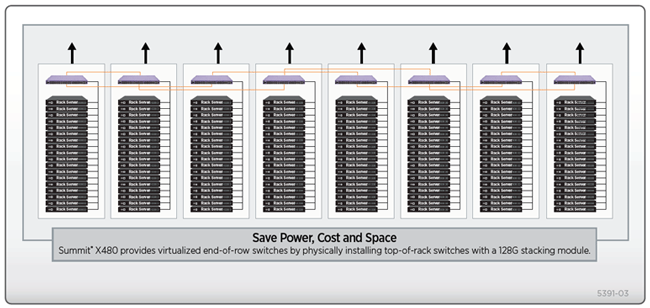 Figure 3: SummitStack Across Racks in a Row
Figure 3: SummitStack Across Racks in a Row
Supports Virtualized Data Centers
Summit X480 switches also support Direct Attach™, which eliminates the virtual switch layer, simplifying the network and improving performance. Direct Attach enables data center simplification by reducing network tiers from 4 or 5 tiers to just 3 or 2 tiers, depending on the size of the data center. To further enhance data center operations, Summit X480 switches support XNV™ (ExtremeXOS Network Virtualization), a set of software modules for the ExtremeXOS based switching product portfolio, and available via the Data Center Feature Pack for Extreme Networks Ridgeline™, a network and service management application. XNV brings insight, control and automation for highly virtualized data centers to the network.
Intelligent Switching and MPLS/ H-VPLS Support
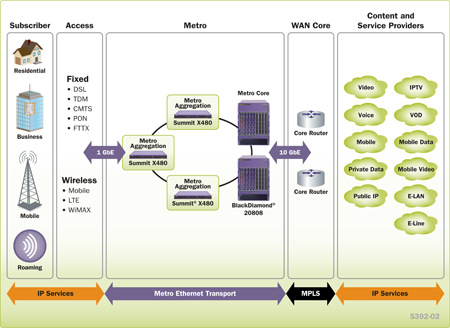
Summit X480 supports sophisticated and intelligent Layer 2 switching, as well as Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 routing including policy-based switching/routing, Provider Bridges, bidirectional ingress and egress Access Control Lists, and bandwidth control by 8 Kbps granularity both for ingress and egress. To provide scalable network architectures used mainly for Carrier Ethernet network deployment, through a feature pack Summit X480 supports MPLS LSP based Layer 3 forwarding and Hierarchical VPLS (H-VPLS) for transparent LAN services. With H-VPLS, transparent Layer 3 networks can be extended throughout the Layer 3 network cloud by using a VPLS tunnel between the regional transparent LAN services typically built by Provider Bridges (IEEE 802.1ad) technology (see Figure 5: Summit X480 in a Carrier Ethernet application).
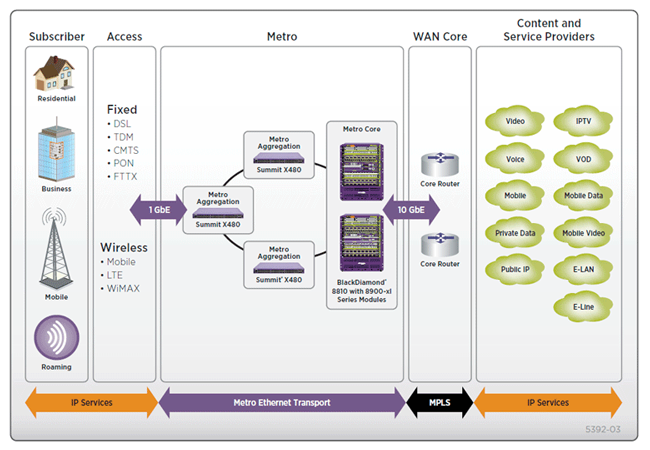
Figure 5: Summit X480 in a Carrier Ethernet Application
High Scalability in 1RU Compact Switch
Summit X480 supports highly scalable Layer 2 or Layer 3 support up to 512K MAC addresses. Similarly for larger Layer 3 networks, as well as highly secure networks. Summit X480 has routing environments, Summit X480 can support core routing expansion memory called TCAM built inside which can be class scalability for up to 512K IPv4 routing LPM entries in partitioned by application types or by deployment scenarios. hardware (See Figure 4: Summit X480 scalability). For larger Layer 2 network deployments, Summit X480 can
| Type | L2 MAC | L3 Host (IPv4/v6) | L3 LPM Route (IPv4/v6) | ACL (Ingress/Egress) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Power Mode | 32K | 16K/8K | 16K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Default (Layer 2+Layer 3) | 256K | 16K/8K | 256K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Large Layer 2 Network Configuration | 512K | 16K/8K | 16K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Large Layer 3 Network Configuration | 32K | 16K/8K | 512K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Security Configuration | 32K | 16K/8K | 16K/8K | 60K/1K |
Figure 4: Summit X480 Scalability
High Availability
Powered by the ExtremeXOS OS, Summit X480 supports process recovery and application upgrades without the need for a system reboot. Summit X480 provides the high network availability required for mission-critical servers and applications through its advanced modular OS, highly available hardware architecture and carrier-grade network redundancy protocols.
Modular Operating System for Continuous Operation
Preemptive Multitasking and Protected Memory
Summit X480 series switches allow each of many applications-such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)-to run as separate OS processes that are protected from each other. This drives increased system integrity and inherently protects against DoS attacks.
Process Monitoring and Restart
ExtremeXOS increases network availability using process monitoring and restart. Each independent OS process is monitored in real time. If a process becomes unresponsive or stops running, it can be automatically restarted.
Loadable Software Modules
The modular design of ExtremeXOS OS allows the upgrading of individual software modules, should this be necessary, leading to higher availability in the network (See Figure 7: ExtremeXOS modular design).
High Availability Network Protocols
Ethernet Automatic Protection Switching (EAPS)
EAPS allows the IP network to provide the level of resiliency and uptime that users expect from their traditional voice network. EAPS is more adaptable than Spanning Tree or Rapid Spanning Tree Protocols and offers sub-second (less than 50 milliseconds) recovery that delivers consistent failover regardless of the number of VLANs, network nodes or network topology. Since EAPS allows the network to recover almost transparently, Voice-over-IP (VoIP) calls will not drop and digital video feeds will not freeze or pixelize in most situations.
Spanning Tree/Rapid Spanning Tree Protocols
Summit X480 supports Spanning Tree (802.1D), Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST+), Rapid Spanning Tree (802.1w) and Multiple Instances of Spanning Tree (802.1s) protocols for Layer 2 resiliency.
Software-Enhanced Availability
Software-enhanced availability allows users to remain connected to the network even if part of the network infrastructure is down. Summit X480 continuously checks for problems in the uplink connections using advanced Layer 3 protocols such as OSPF, VRRP and Extreme Standby Router Protocol™ (ESRP, supported in Layer 2 or Layer 3), and dynamically routes traffic around the problem.
Equal Cost Multipath
Equal Cost Multipath (ECMP) routing allows uplinks to be load balanced for performance and cost savings while also supporting redundant failover. If an uplink fails, traffic is automatically routed to the remaining uplinks and connectivity is maintained.
Link Aggregation (802.3ad)
Link aggregation (LAG) allows trunking of up to eight links on a single logical connection. A maximum of 128 link aggregation groups can be created.
Multi-Switch LAG (M-LAG)
M-LAG can address bandwidth limitations and improve network resiliency, in part by routing network traffic around bottlenecks, reducing the risks of a single point of failure, and allowing load balancing across multiple switches.
Voice-Grade Stacking with SummitStack
All SummitStack stacking architecture is designed to support mission-critical applications by its highly available, rapid failover capability with n-1 master redundancy, distributed Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching, link aggregation across the stack, and distributed uplinks. SummitStack supports up to eight units in a stack, including any mix of Summit X650, X480, X460, X450a, X450e and X250e running the same version of ExtremeXOS and provides 50 milliseconds failover for path failure and hitless master/backup failover along with hitless protocol support such as OSPF graceful restart and Network Login user authentication.
Alternatively, you may choose high-speed 80 Gbps stacking, which is ideal for demanding applications where a high volume of traffic traverses through the stacking links, yet bandwidth is not compromised through stacking. SummitStack-V80 also breaks the distance limitation for stacking technology by using QSFP+ technology. SummitStack-V80 can support passive copper cable (up to 5m), active multi-mode fiber cable (up to 100m), and QSFP+ optical transceivers which will be the standard technology for 40 GbE. With SummitStack-V80, the Summit X460 provides a flexible stacking solution inside the data center or central office to create a virtualized switching infrastructure across rows of racks. SummitStack-V80 is compatible with Summit X460, X480 and X670V switches running the same version of ExtremeXOS.
Summit X480 provides chassis-like management and availability with its SummitStack stacking technology (See Figure 8: SummitStack stacking architecture).
Hardware Redundancy
Summit X480 supports a dual redundant AC/DC power supply to provide high availability. The power supply can be hot-swapped and replaced should it fail. Summit X480 supports a hot-swappable, field replaceable fan.
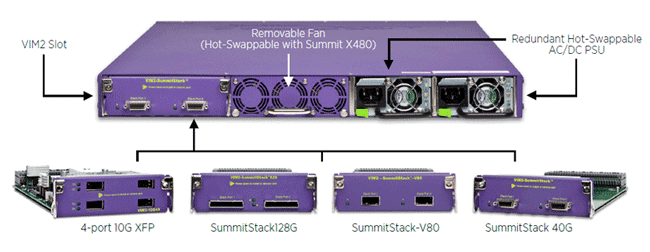 Figure 6: Summit X480 High Availability Design
Figure 6: Summit X480 High Availability Design
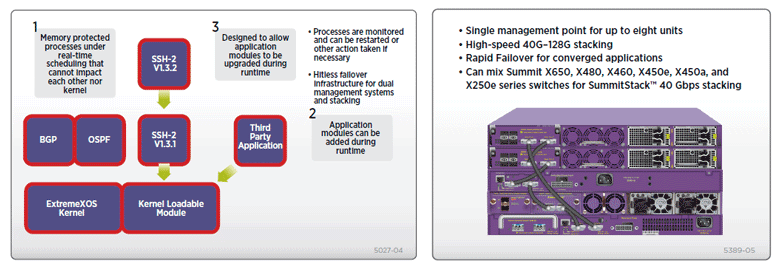 Figure 7: ExtremeXOS Modular Design Figure 8: SummitStack Stacking Architecture
Figure 7: ExtremeXOS Modular Design Figure 8: SummitStack Stacking Architecture
Comprehensive Security Management
Implementing a secure network means providing protection at the network perimeter as well as the core. Summit X480 uses advanced security functions in protecting your network from known or potential threats.
Robust IP and MAC Security Framework
NetLogin
Network Login provides three types of authentication-Webbased, MAC-based, and 802.1x-to properly authenticate network users against RADIUS servers. When combined with Extreme Networks Universal Port Manager (UPM), IT administrators can dynamically provision policies to associated network users based on roles or UPM profiles.
Media Access Control (MAC) Security
MAC security allows the lockdown of a port to a given MAC address and limiting the number of MAC addresses on a port. This can be used to dedicate ports to specific hosts or devices and avoid abuse of the port. In addition, an aging timer can be configured for the MAC lockdown, protecting the network from the effects of attacks using (often rapidly) changing MAC addresses.
IP Security
ExtremeXOS IP security framework protects the network infrastructure, network services and host computers from rogue access, spoofing and man-in-the-middle attacks. It also protects the network from statically configured and/or spoofed IP addresses and builds an external trusted database of MAC/IP/port bindings providing the traffic's source from a specific address for immediate defense.
Identity Manager
Identity Manager allows network managers to track users who access their network. User identity is captured based on NetLogin authentication, LLDP discovery and Kerberos snooping. ExtremeXOS uses the information to then report on the MAC, VLAN, computer hostname, and port location of the user. Further, Identity Manager can create both roles and policies, and then bind them together to create role-based profiles based on organizational structure or other logical groupings, and apply them across multiple users to allow appropriate access to network resources.
Private VLANs
Private VLANs provide port-to-port security to prevent unauthorised communication of users within the same VLAN. Unlike normal VLANs, ports enabled for Private VLANs cannot communicate with other ports in the same VLAN over Layer 2 or Layer 3. Private VLAN ports can only communicate with a designated "uplink" port. In addition, a Private VLAN provides separation of broadcast domains within the same VLAN.
Threat Detection and Response
CLEAR-Flow Security Rules Engine
CLEAR-Flow provides first order threat detection and mitigation, and mirrors traffic to appliances for further analysis of suspicious traffic in the network.
Protocol Anomaly Detection
The Extreme Networks chipsets contain built-in hardware protocol checkers that support port security features for security applications, such as stateless DoS protection. The protocol checkers allow users to drop the packets based on conditions, which are checked for ingress packets prior to the Layer 2/Layer 3 entry table.
sFlow
sFlow® is a sampling technology that provides the ability to sample application-level traffic flows on all interfaces simultaneously.
IPFIX
IPFIX (Internet Protocol Flow Information eXport) defines an Internet standards-track protocol for a follow-on protocol to the proprietary Netflow. The technology is a complementary protocol to sFlow. IPFIX gathers information about network flows through the switch and sends the information to an external collector. Summit X480 includes hardware support to keep track of the flow records.
Port Mirroring
Summit X480 supports many-to-one and one-to-many port mirroring. This allows the mirroring of traffic to an external network appliance such as an intrusion detection device for trend analysis or for utilization by a network administrator for diagnostic purposes. Port mirroring can also be enabled across switches in a stack.
Line-Rate ACLs
ACLs are one of the most powerful components used in controlling network resource utilization as well as protecting the network. ACLs are used for filtering the traffic, as well as classifying the traffic flow to control bandwidth, priority, mirroring, and policy-based routing/switching.
Denial of Service Protection
Summit X480 effectively handles Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. If the switch detects an unusually large number of packets in the CPU input queue, it assembles ACLs that automatically stop these packets from reaching the CPU. After a period of time, these ACLs are removed, and reinstalled if the attack continues.
Secure and Comprehensive Network Management
Summit X480 supports comprehensive network management through Command Line Interface (Cli), SNMP v1, v2c, v3, and ExtremeXOS ScreenPlay™ embedded XML-based Web user interface. With a variety of management options and consistency across other Extreme Networks modular and stackable switches, Summit X480 series switches provide ease of management for demanding converged applications.
Extreme Networks has developed tools that simplify and help in efficiently managing your network. Ridgeline network and service management provides fault, configuration, accounting, performance and security functions, allowing more effective management of Extreme Networks products, solutions and third-party devices, in a converged network.
For carrier networks, Ridgeline enables the shift from reactive circuit monitoring to proactive service management. The key features integrated into the Service Advisor Feature Pack unify service fulfillment, service assurance and service engineering to enable carriers to more effectively manage next-generation residential triple play, business Ethernet and Ethernet mobile backhaul services.
Network Diagram:
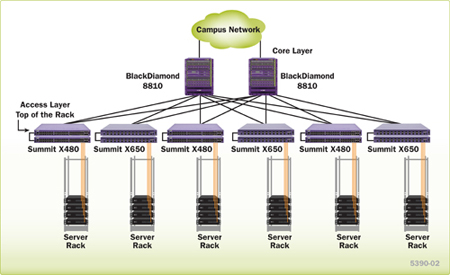
Top of the rack switch for servers in the enterprise data centers
In the enterprise data center, many servers and storage systems are packed in racks, with all systems needing high-speed connectivity. A top-of-rack architecture is one way to simplify the cabling infrastructure and minimize the space requirements in the enterprise data center. Summit X480 is optimized to support high density Gigabit Ethernet connectivity for servers and other network attached devices and provides high-speed 128Gbps stacking connectivity with Summit X650 10 Gigabit Ethernet switch to provide the hybrid deployment for both gigabit and 10 Gigabit enabled servers in the data centers.
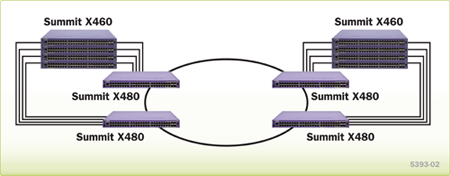
High-performance 10 gigabit core switch for a small network and aggregation switch in a traditional three-tiered network
Summit X480 offers enterprise-core class scalability for both Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching. Summit X480 can support up to 512,000 Layer 2 MAC addresses or 512,000 IPv4 longest prefix matching routes. The Summit X480 switch can also be used in the network aggregation layer in an enterprise network. With its versatile design, Summit X480 simplifies enterprise network deployment.
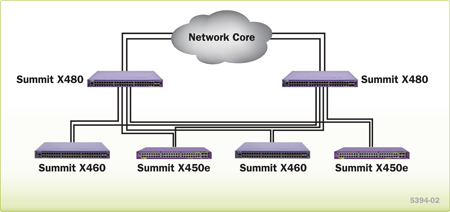
Carrier Ethernet network switch that can aggregate connectivity for first mile access concentrators
Summit X480 is an ideal service delivery platform for Carrier Ethernet networks. The advanced traffic management, resiliency and scalability features give it the flexibility to be deployed at the Provider Edge or as an aggregation switch. By supporting highly scalable Layer-2 and Layer-3 features along with MPLS/H-VPLS in hardware, Summit X480 simplifies the network deployment.
Specifications:
| X480 Series Specification | |
|---|---|
| General Specifications | |
| Performance |
|
| Forwarding Tables and ACLs | Summit X480 provides flexible configuration options for various deployments. |
| CPU, Memory |
|
| QoS, Rate Limiting |
|
| LED Indicators |
|
| External Ports |
|
| External Ports for VIM2 Modules |
|
| Option Slots | Slot for Versatile Interface Module 2 (VIM2) available for Summit X480-24x, Summit X480-48t and Summit X480-48x |
| Power Supply Support | Summit X480 AC PSU and Summit X480 DC PSU |
| Fan Speed |
|
| Physical Specifications | |
| Physical Dimensions |
|
| Weight |
NOTE: Switch weights include installed fan module. They do not include installed VIM2 modules or PSUs.
|
| Operating Specifications | |
| Operating Temperature Range | 0° C to 45° C (32° F to 113° F) |
| Operating Humidity | 10% to 93% relative humidity, non-condensing |
| Operating Altitude | 0-3,000 meters (9,850 feet) |
| Operational Shock (Half Sine) | 30 m/s2 (3 g), 11ms, 60 Shocks |
| Operational Random Vibration | 3-500 MHz @ 1.5g rms |
| Storage & Transportation Conditions (Packaged) | Yes |
| Transportation Temperature | -40° C to 70° C (-40° F to 158° F) |
| Storage & Transportation Humidity | 10% TO 95% RH, Non-Condensing |
| Packaged Shock (Half Sine) | 180 m/s2 (18 G), 6ms, 600 shocks |
| Packaged Sine Vibration | 5-62 Hz @ Velocity 5mm/s, 62-500 Hz @ 0.2G |
| Packaged Random Vibration | 5-20 Hz @ 1.0 ASD w/-3dB/oct. from 20-200 Hz |
| Sides & Corners | 14 drops min on sides corners @ 42" (<15 kg box) |
| Safety Standards | |
| North American Safety of ITE |
|
| European Safety of ITE |
|
| International Safety of ITE |
|
| EMI/EMC Standards | |
| North America EMC Standards |
|
| European EMC Standards |
|
| International EMC Standards |
|
| Country Specific |
|
| Telecom Standards |
|
| IEEE 802.3 Media Access Standards |
|
| Environmental Standards |
|
| Warranty |
|
| Type | L2 MAC | L3 Host (IPv4/v6) | L3 LPM Route (IPv4/v6) | ACL (Ingress/Egress) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Power Mode | 32K | 16K/8K | 16K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Default (Layer 2+Layer 3) | 256K | 16K/8K | 256K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Large Layer 2 Network Configuration | 512K | 16K/8K | 16K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Large Layer 3 Network Configuration | 32K | 16K/8K | 512K/8K | 8K/1K |
| Security Configuration | 32K | 16K/8K | 16K/8K | 60K/1K |
ExtremeXOS 12.5 Supported Protocols
Switching
Management and Traffic Analysis
Security, Switch and Network Protection
Security, Router Protection
Security Detection and Protection
IPv4 Host Services
IPv4 Router Services
|
IPv6 Host Services
IPv6 Interworking and Migration
IPv6 Router Services
Core Protocols for Layer 2, IPv4 and IPv6 Requires Core License
Quality of Service and Policies
Traffic Engineering
VLAN Services: VLANs, vMANs
Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) Requires MPLS Feature Pack License
Layer 2 VPNs Requires MPLS Feature Pack License
Data Center
|
Power Specifications:
| Summit X480-24x | |
|---|---|
| Summit X480-24x with No Installed VIM (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-24x with VIM2-SummitStack Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-24x with VIM2-10G4X Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-24x with VIM2-SummitStack128 Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-24x with No Installed VIM (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-24x with VIM2-SummitStack Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-24x with VIM2-10G4X Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-24x with VIM2-SummitStack128 Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x | |
| Summit X480-48x with No Installed VIM (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x with VIM2-SummitStack Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x with VIM2-10G4X Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x with VIM2-SummitStack128 Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x with No Installed VIM (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x with VIM2-SummitStack Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x with VIM2-10G4X Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48x with VIM2-SummitStack128 Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t | |
| Summit X480-48t with No Installed VIM (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t with VIM2-SummitStack Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t with VIM2-10G4X Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t with VIM2-SummitStack128 Module (AC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t with No Installed VIM (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t with VIM2-SummitStack Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t with VIM2-10G4X Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
| Summit X480-48t with VIM2-SummitStack128 Module (DC Power Supply) |
|
Power Supply Units
| Summit X480 AC PSU | |
|---|---|
| For use with the Summit X480-24x, Summit X480-48x, and Summit X480-48t switches | |
| Physical Specifications |
|
| Power Specifications |
|
| Summit X480 DC PSU | |
| For use with the Summit X480-24x, X480-48x, and X480-48t switches | |
| Physical Specifications |
|
| Power Specifications |
|
Documentation:
Download the Extreme Networks Summit X480 Series Datasheet (.PDF)
Pricing Notes:
- All Prices are Inclusive of GST
- Pricing and product availability subject to change without notice.
48 10/100/1000BASE-T, 4 100/1000BASE-X unpopulated SFP (shared), No PSU with two unpopulated PSU slots, one VIM2 slot, ExtremeXOS Advanced Edge license
Our Price: Request a Quote
48 100/1000BASE-X unpopulated SFP, No PSU with two unpopulated PSU slots, one VIM2 slot, ExtremeXOS Advanced Edge license
Our Price: Request a Quote

